Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) is a powerful analytical technique used to determine the structure, dynamics and reaction kinetics by monitoring chemical environment of molecules. By placing a sample in a strong magnetic field and applying radio-frequency pulses, NMR is able to manipulate magnetic moments of nuclei, particularly hydrogen (¹H) and carbon (¹³C), but also others such as fluorine (19F) or phosphorous (31P), which in the recorded signal reveal detailed information about the molecular structure and interactions.
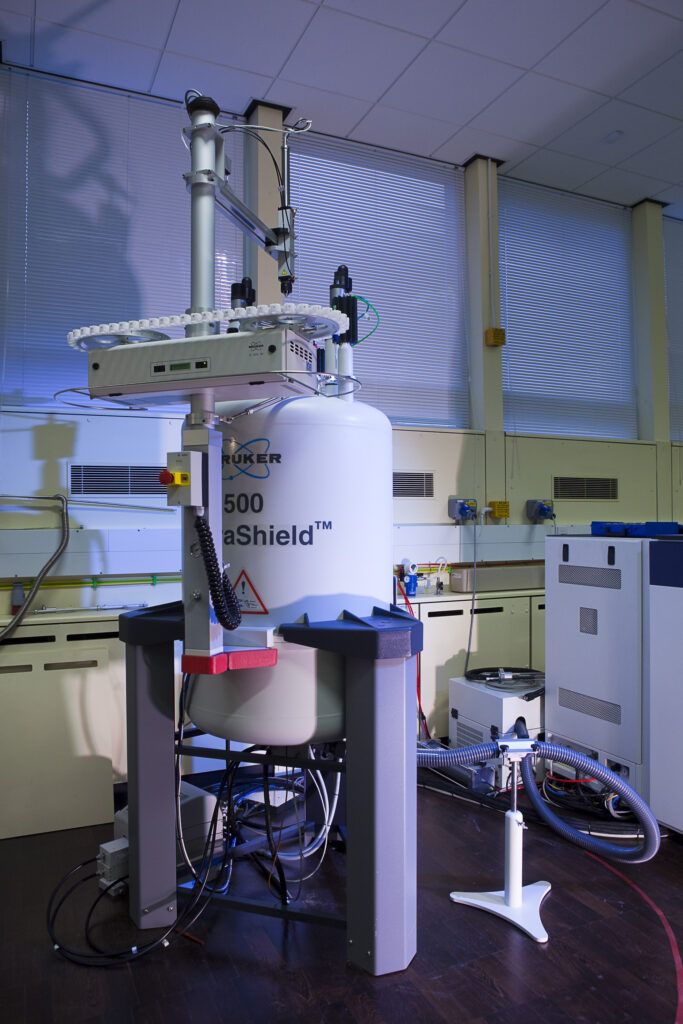
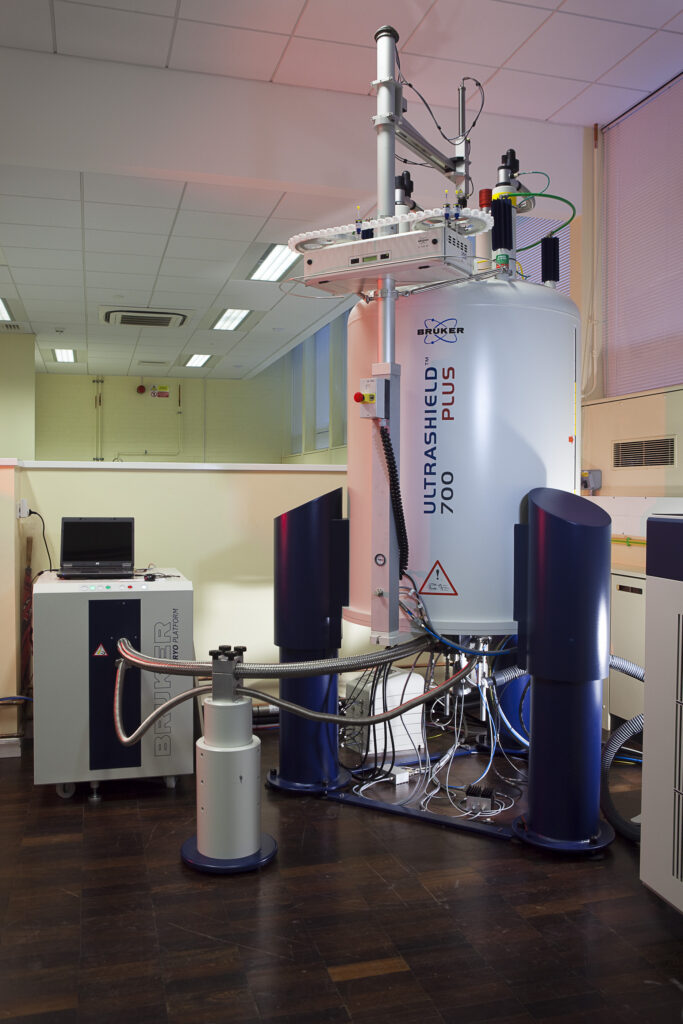
The NMR instruments in CAF can conduct wide range of solution (HR-NMR), intact gels/tissues (HRMAS) and solid-state (MAS) NMR experiments. CAF offers both a routine automated service as well as the potential for collaborative NMR expertise to scientists throughout the University and external users.
Our superconductive magnets contain large amounts of cryogenic liquids and operate at high magnetic fields. Therefore, all who enter the NMR laboratory should be familiar with risks and safety procedures.