Knowledge Base
- /
- /
 Reading Academic Computing Cluster – Introduction
Reading Academic Computing Cluster – Introduction
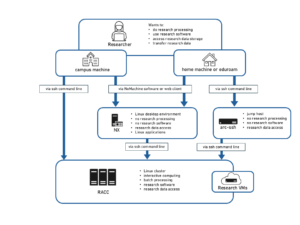
The Reading Academic Computing Cluster (RACC) is a Linux cluster which provides resources for interactive research computing and batch job submissions for staff and students of the University of Reading.
Most of the cluster resources are available for free for all members of UoR, with some additional nodes that are funded and used by research projects. New: project-funded nodes can be requested in the Self Service Portal.
Introduction to the Reading Academic Computing Cluster
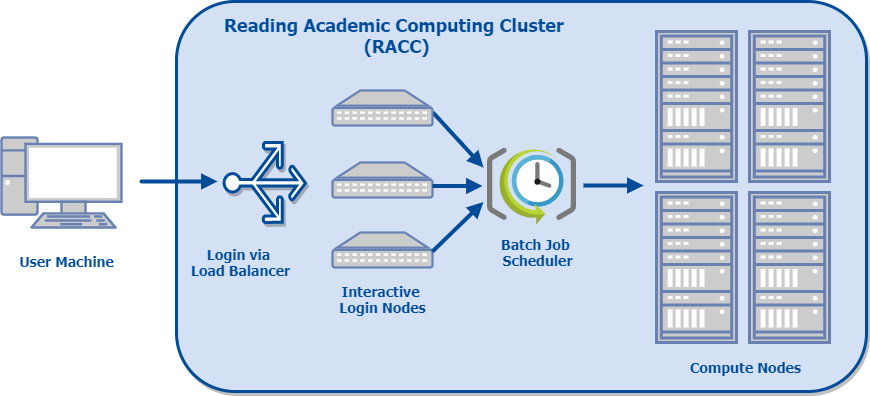
The cluster consists of several login nodes and a larger number of compute nodes. On a typical cluster, login nodes are only used for preparing and submitting batch jobs. On the RACC however, we provide several load-balanced login nodes equipped with multi-core processors, large memory and a fast network connection to the research data storage volumes, so that they can also be used for interactive research computing, such as data analysis and visualization, or code development and testing.
In batch mode the tasks are described in a script and submitted to the job scheduler to be run on one of the compute nodes without further user intervention. The compute nodes provide around 1000 CPU cores for serial and parallel batch jobs. The default time limit for a batch job is 24 hours, but when it is justified, running longer batch jobs is also possible. When justified by the project requirements, it is also possible to use a compute node allocation for interactive processing.
Typically users rely on home directories for small storage needs and on chargeable Research Data Storage volumes for large storage requirements. There is also a 150 TB scratch space, which is available for free but access it provided on request via the DTS self service portal.
This diagram shows a schematic layout of the RACC:
A comprehensive list of installed software can be found here.
Technical Details of free resources on the RACC:
| Number of login nodes | 5 |
| Login node specs | 24 CPU cores, 256 GB of memory |
| Number of compute nodes | around 100 |
| Number of cores per node | from 8 to 24 |
| Total number of CPU cores | around 1300 |
| Memory per core | typically 6 GB |
| Scratch space | 150 TB |