Knowledge Base
- /
- /
- /
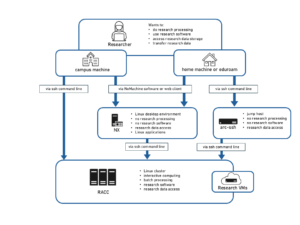
 Research data transfer using arc-ssh.reading.ac.uk
Research data transfer using arc-ssh.reading.ac.uk
Transferring files using SSH based tools: scp, sftp and rsync
arc-ssh is an externally accessible server. All UoR users can set up two factor authentication to arc-ssh and use it to transfer files to and from the UoR Unix system. If you set up Google Authenticator authentication as the second authentication step, you will be able to use the scp, sftp, and rsync based tools as usual, but you will need to provide both the verification code and then the UoR password to authenticate. If you want to avoid entering the password and the verification code multiple times, we suggest using ssh connection caching (on Linux and Mac). See the arc-ssh instructions for more details.
See below for some examples of using scp, sftp and rsync.
SCP:
pawel@home-PC:~$ scp testfile.txt qx901702@arc-ssh.reading.ac.uk:/home/users/qx901702/ Verification code: Password: testfile.txt 100% 0 0.0KB/s 00:00 pawel@home-PC:~$
SFTP:
pawel@home-PC:~$ sftp qx901702@arc-ssh.reading.ac.uk Verification code: Password: Connected to arc-ssh.reading.ac.uk. sftp> put testfile.txt Uploading testfile.txt to /home/users/qx901702/testfile.txt testfile.txt 100% 0 0.0KB/s 00:00 sftp> quit pawel@home-PC:~$
RSYNC:
pawel@home-PC:~$ rsync -av testdir qx901702@arc-ssh.reading.ac.uk:/home/users/qx901702/ Verification code: Password: sending incremental file list testdir/ testdir/testfile.txt sent 146 bytes received 39 bytes 370.00 bytes/sec total size is 0 speedup is 0.00 pawel@home-PC:~$
This can be automated by specifying the act-ssh port in the personal ssh configuration file, see arc-ssh for Linux and Mac users – step by step guide.
arc-ssh allows access to SMB shares (collabs, ndrive, SMB RDS), such that you can use an sftp client from off-campus to access data in your SMB shares, as well as in your NFS shares.
arc-ssh does not allow to share data with external collaborators.