Ensuring long-term integrity of financial transactions using Blockchain-as-a-Service integrity component
By Tuuli Lõhmus, Project Manager, Guardtime

The banking sector is being increasingly regulated to counter money laundering, illicit transactions, and unaudited activities. Stricter regulations often affect banking operations as customers are faced with increasingly complex solutions and burdensome services. Emerging digital technologies promise to provide solutions to the problem, allowing user-friendly financial transactions and operations to continue. This requires secure and swift customer data exchange between banks and other financial operators while ensuring the highest level of privacy and data protection.
One of the emerging digital technologies that has yet to reach its full potential are blockchain-based components. In the Critical Chains project, the Blockchain-as-a-Service (BCaaS) component enables swift use of blockchain for financial transaction recording and enables smart contract implementations. This is done using Quorum, an Ethereum based blockchain. In addition to Quorum, a second blockchain – KSI Blockchain – is used to ensure integrity and auditability of all financial transactions. Guardtime’s KSI Blockchain has been in continuous operation for over 13 years and is highly scalable.
KSI Signatures which are linked to KSI Blockchain are used to sign and secure the data-hash roots produced by financial transactions taking place over the network. Hash can be thought of as a fingerprint of the data, which contains none of the information about the content but provides a strong link to the data. Like humans, having a fingerprint gives no information about the person it belongs to. Hash functions are one-way functions and preserve data privacy. KSI Blockchain is a permissioned scheme which relies on a proprietary consensus protocol, providing the following properties to BCaaS:
- Data integrity – a KSI signature links input data to a verifiable, distributed trust-anchor using a one-way hash chain.
- Signing time – a KSI signature provides strong proof of signing time.
- Signing entity – a KSI signature provides attestation of origin. When the system aggregates a set of input data hashes, as part of the formation of a new node (or block) for the blockchain, the identities of all participants (from customer applications to Blockchain core servers) are tied to it. As such, these identities are also embedded in the signature.
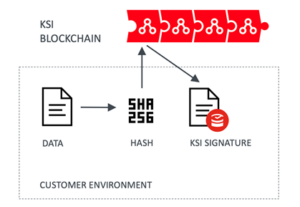
Data never leaves the customers’ environment (for example bank), only the data hash is recorded in the KSI Blockchain.
The mechanism provides the ability to verify the integrities of financial transactions against the distributed ledger of the KSI Blockchain. These guarantees are available over the long-term where events can be independently verified many years later.
All in all, through its use of KSI signatures, KSI Blockchain provides independently verifiable proofs of integrity, signing time and signing entity. The process also ensures data privacy for all the financial transactions. BCaaS with its integrity component enables secure and auditable financial transactions. We believe trust, integrity and auditability are an integral part of any future system and service.
Photo by Jason Pofahl on Unsplash.
